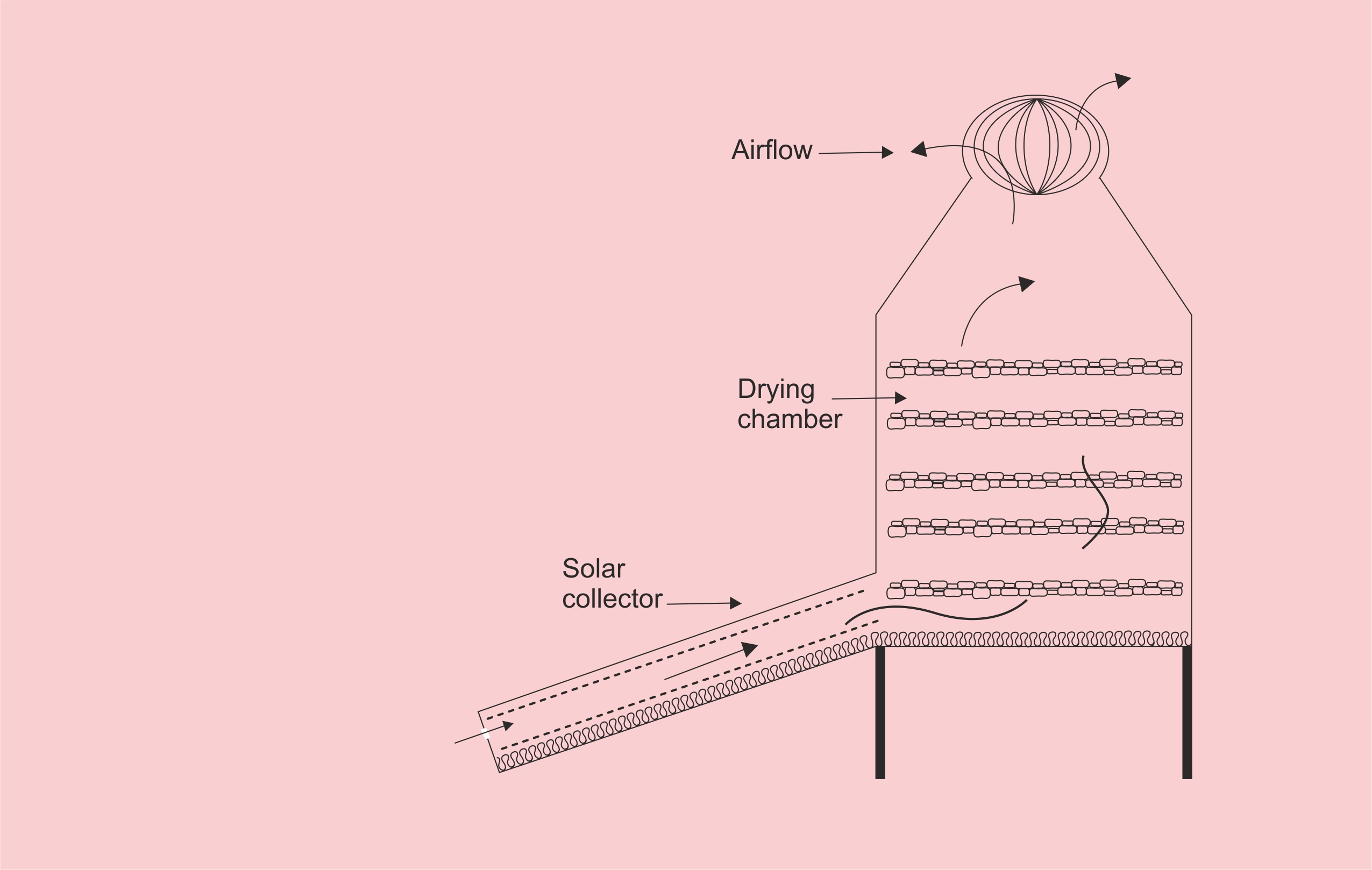
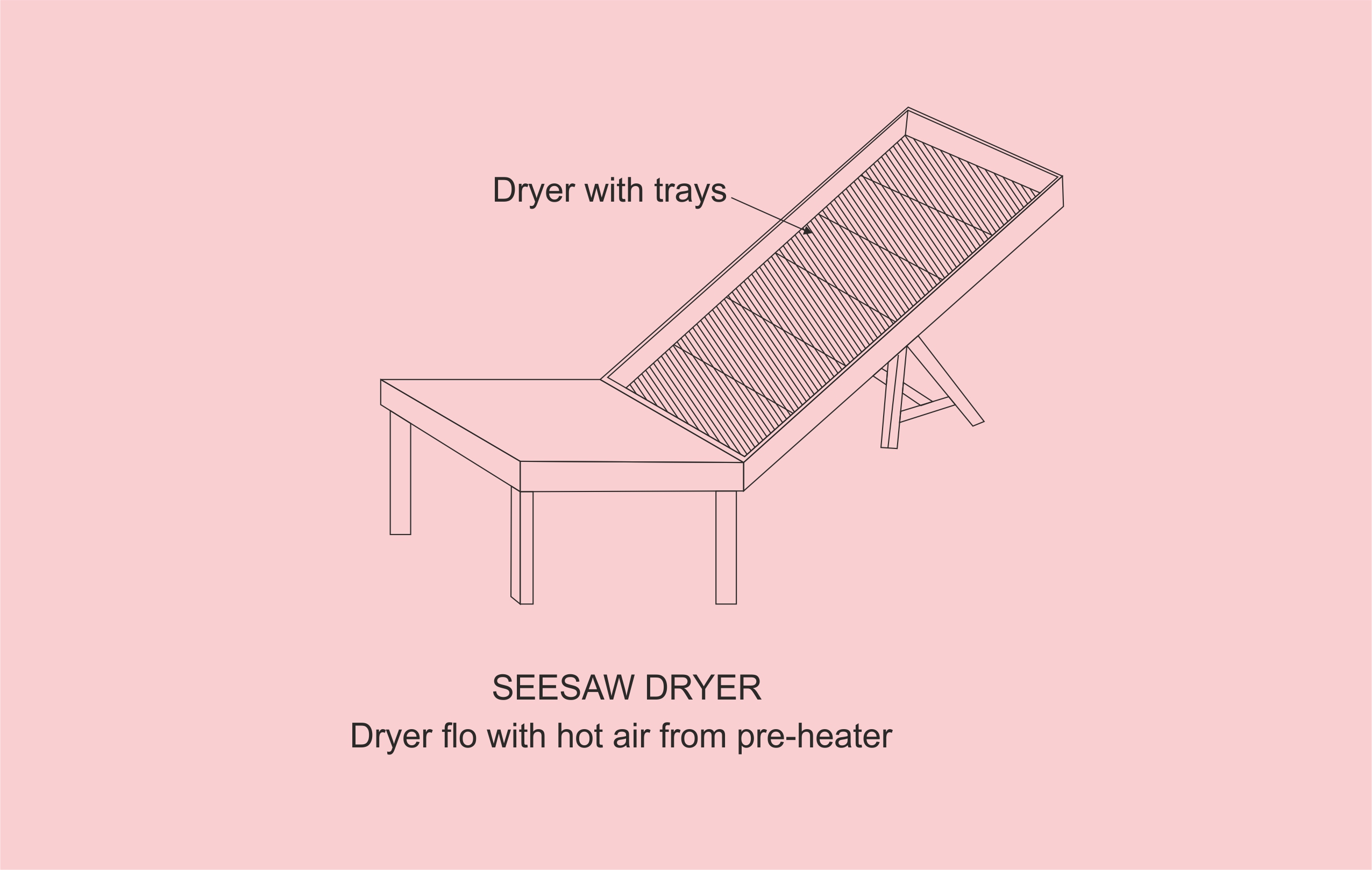
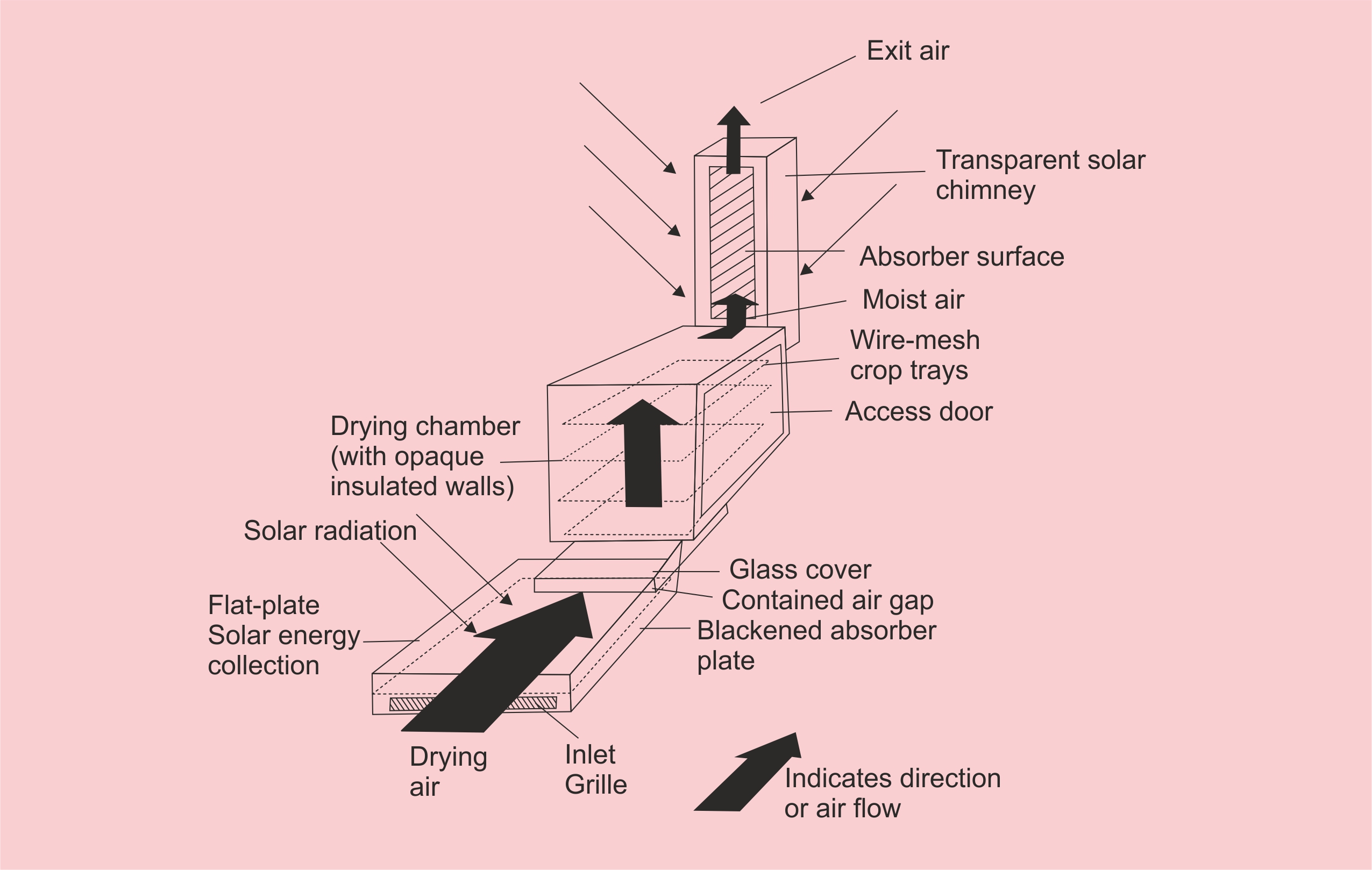
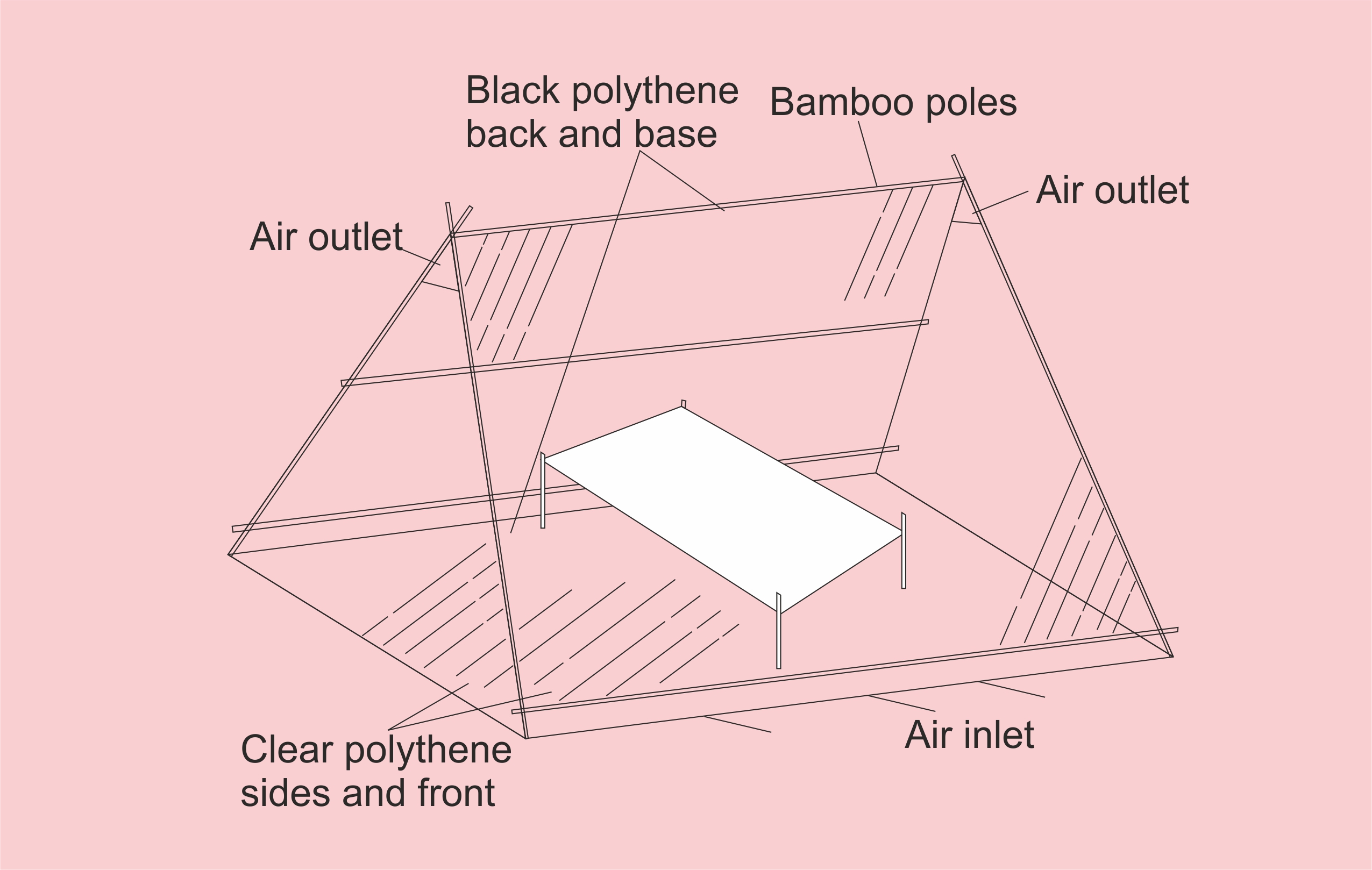
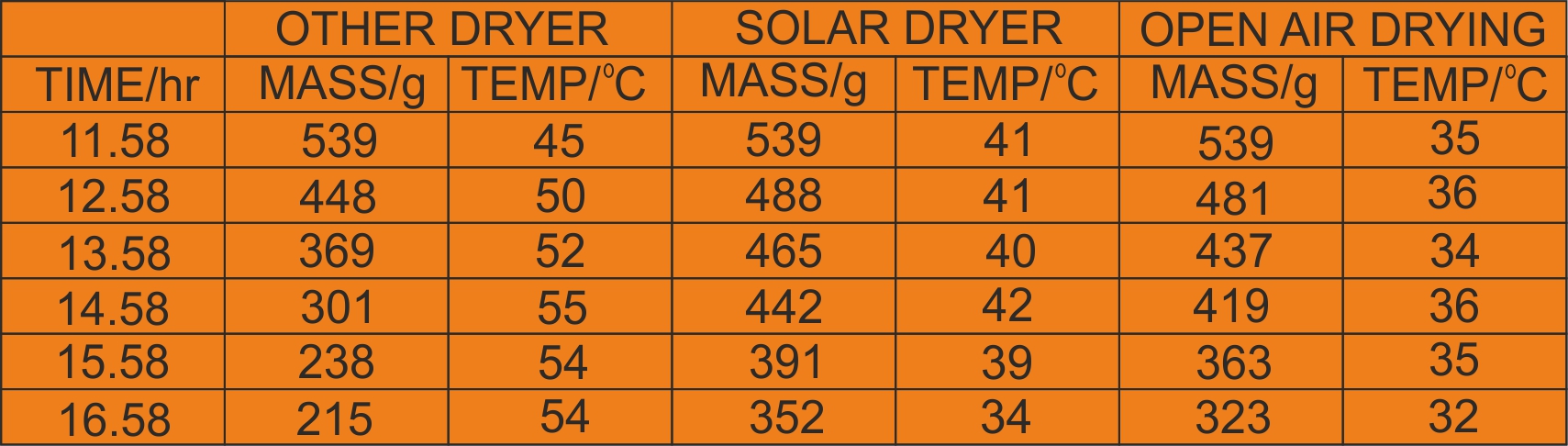
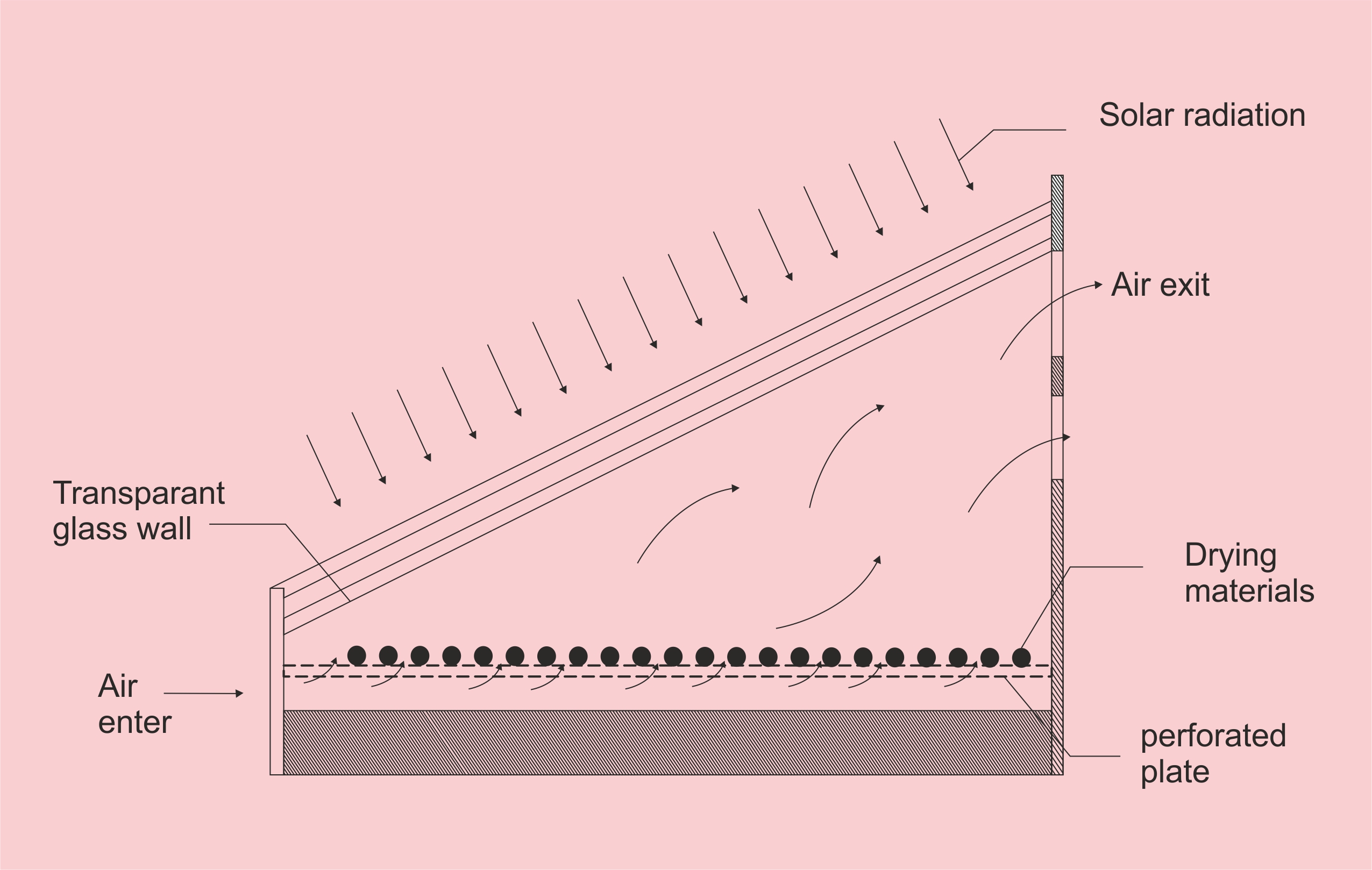
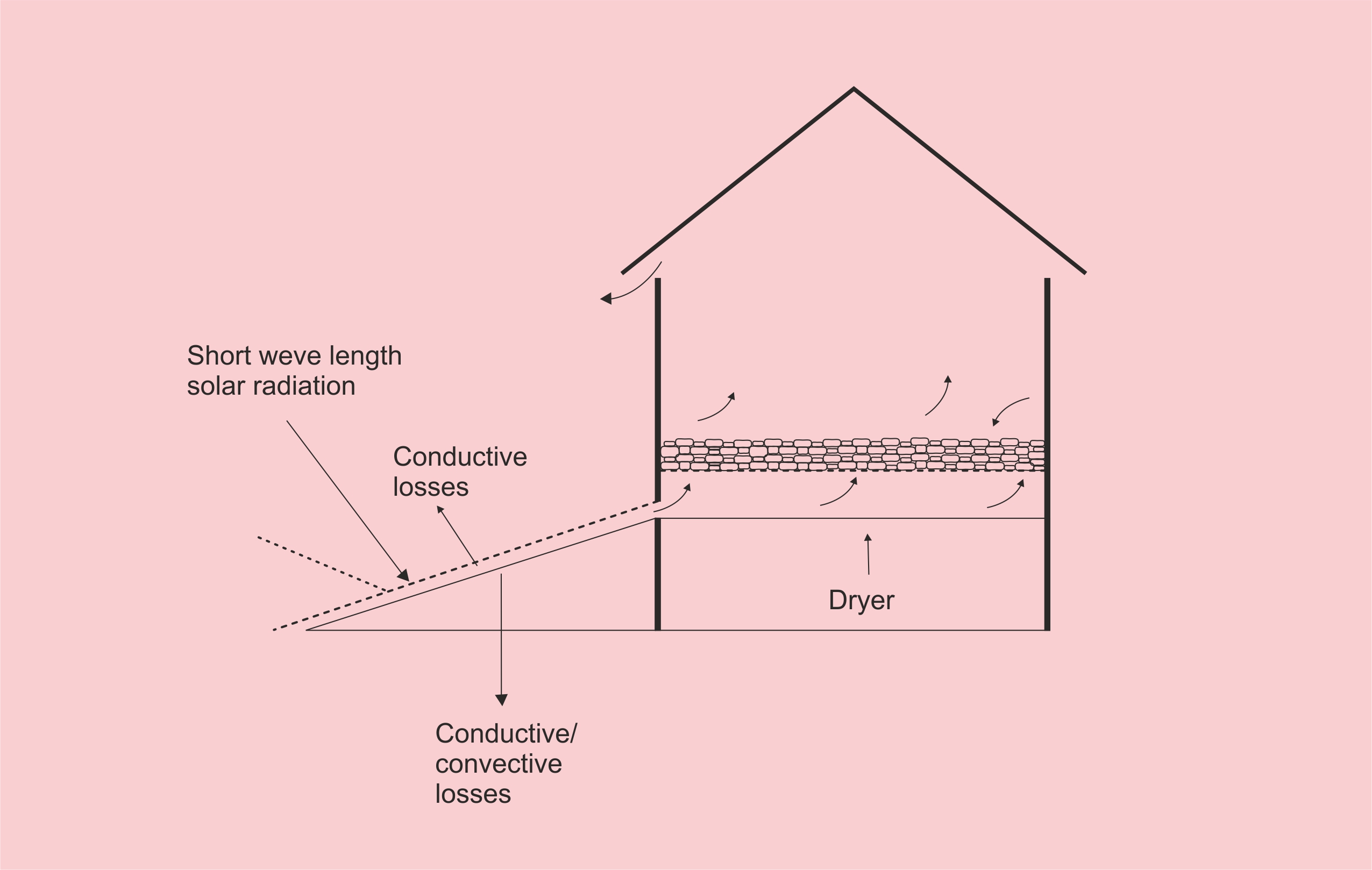
Sun drying of agricultural products is the traditional method employed in most of the developing countries. Sun drying is used to denote the exposure of a commodity to direct solar radiation and the convective power of the natural wind. Sun drying offers a cheap method of drying but often results to inferior quality of products due to its dependence of weather conditions and vulnerably to the attack of dust, dirts, rains, insects, pests, and microorganisms. Solar drying is an alternative which offers several advantages over the traditional method and it has been developed for various agricultural products. Solar energy for crop drying is environmentally friendly and economically viable in the developing countries
In natural convection solar dryers, the air flow is due to buoyancy-induced air pressure, and the drying process needs some days to complete, as a cabinet dryer needs 3–4 days to dry grapes.While in forced convection solar dryers the air flow is provided by using a fan either operated by electricity/solar module or fossil fuel. Some researchers are opting for forced convection solar tunnel drying for drying of various crops. They reported that solar drying for grapes during the night period, it is necessary to develop a system having a back-up of thermal storage. An auxiliary heat and forced convection are recommended for assuring reliability and better control, respectively. However, there exist some problems associated with solar drying i.e. reliability of solar radiation during rainy period or cloudy days and its unavailability at nighttime. In a hybrid solar dryer, drying is continued during offsunshine hours by back-up heat energy or storage heat energy. Therefore, drying is continued and the product is saved from possible deterioration by microbial infestation . Variability and time-dependent characteristic of solar radiation make storage necessary for continuous operations of food drying . The operation of a solar assisted dryer extended through the night hours and found that thermal storage during the day can be used as a heat source during the night for continuing drying of agricultural products and also preventing their re-hydration from the surrounding air . Continuous drying also prevents microbial growth during drying . Also, it was found that storage and auxiliary heat supply can used to assess compatibility of solar energy to meet the drying process temperature . Misra et al.reported that the advantage of storing solar heat several weeks for use in grain drying was to enable drying to proceed independently of the fall weather conditions. This allowed management flexibility in harvesting and drying the crops. The major disadvantage was that it required more hardware, in the form of a large heat storage structure and heat recovery equipment, which could lead to excessive cost.